
What is a Cross-Chain Bridge and How Does it Work?
A cross-chain bridge is a technology that enables the seamless transfer of digital assets between different blockchain networks. Learn what is a cross-chain...

A cross-chain bridge is a technology that enables the seamless transfer of digital assets between different blockchain networks. Learn what is a cross-chain...
Until a few years ago, people normally did not take blockchain seriously. Today, every person around the world has at least heard of what a blockchain is, and the crypto market has grown rapidly. It is all because of the decentralization, security, and investment opportunities that the blockchain provides. But what is the next step for this technology?
Experts say that developers are trying to tackle the issue of interoperability. Moving forward in this direction, crypto cross-chain bridges have become a blessing for the crypto world. As the name suggests, it helps create a bridge between blockchains, surpassing their protocols, therefore letting the users operate on two chains simultaneously. What is a cross-chain bridge exactly? And how does it provide interoperability? These are the questions that we will be getting into now.
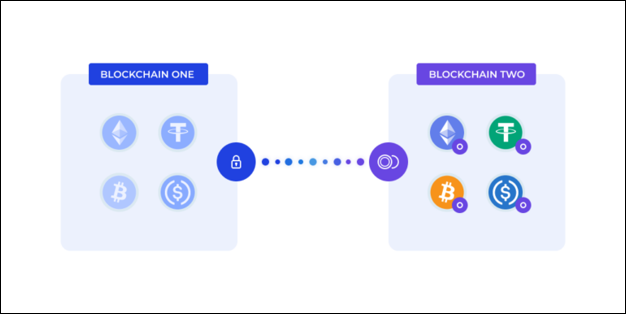
Again, a cross-chain bridge is technology that transfers digital assets or data between two or more different blockchain networks. Blockchain networks like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other blockchain platforms operate independently with a variety of consensus mechanisms, and native assets. A cross-chain bridge is an interoperability solution that enables communication and exchange of assets or data across these different blockchain networks.
Cross-chain bridges typically consist of smart contracts, protocols, or other mechanisms that facilitate the transfer of assets or data across blockchains. They often require a bridge token or native asset representing the transferred value. They may also involve mechanisms like decentralized oracles, validators, and relayers to verify transactions and ensure security and consensus across the participating blockchains.
Cross-chain bridges have become increasingly popular in the blockchain ecosystem because they enable interoperability between different blockchain networks, allowing users to move assets or data seamlessly between chains. They can facilitate various use cases, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, token swaps, cross-chain asset transfers, and more. Cross-chain bridges aim to overcome the limitations of blockchain interoperability, which can unlock new opportunities and use cases in the blockchain space.

Here are the key points on how a cross-chain bridge typically works:
A crypto cross-chain bridge is very important for the current scenario of blockchain technology. Blockchain has allowed people worldwide to earn passive income through careful investments. Earlier the majority of income came from holding assets. Now, options like staking, yield farming, lending pools, etc., make it easier for people to earn returns. The only problem that people have to face is that all of this cannot be done easily without the interoperability of blockchains. A token has to be blockchain compatible for users to stake, lend or even hold it.
Cross-chain bridges add productivity to cryptocurrency by making it possible to use different tokens on a blockchain. Users can even mint NFTs on different blockchains to use as collateral. A crypto cross-chain bridge also offers the chance to enhance the user experience. It does so by offering a chance to use the capabilities of multiple blockchains on each other. For example, the de-facto platform of the ETH chain that offers high security and opportunities to create DApps can now be used with chains like Polygon, Arbitrum, etc.
Also, for a DApp to gain popularity and have more users, they need to have more liquidity. Often, new DApps lack this liquidity due to a lesser audience. Cross-chain bridges help such DApps to get more liquidity. The chains like BTC, ETH, Polygon, etc., have excess liquidity at times. DApp developers can use this liquidity to get a higher TVL. Best cross-chain bridges also offer a chance for developers to create decentralized apps through cross-chain functionalities. The developers can switch between networks whenever they face congestion or problems with UI. All such factors add to the importance of a crypto cross-chain bridge.
As the name suggests, such a crypto cross-chain bridge offers to transfer a single asset between two chains. For example, wBTC is a cryptocurrency that allows the transfer of BTC from the native chain to the ETH chain. Such a cross-chain bridge operates on simple functions and is frequently used.
Now that we are talking about transferring assets between two chains, multiple bridges offer to transfer various assets between two chains. Let’s discuss an example of such a bridge: the Rainbow Bridge. It is a cross-chain bridge that can send ETH and other ERC-20 assets to the NEAR protocol.
Moving forward, many users require the transfer of assets between multiple chains. This kind of crypto cross-chain bridge allows users to connect one chain to multiple other chains. Wormhole is one bridge that offers transferring assets from Solana to chains like Ethereum, Fantom, Avalanche, Terra, and Polygon.
Taking another step into offering interoperability of blockchain networks, some bridges allow users to transfer multiple assets between chains. Such bridges can help developers create DApps that offer higher app liquidity. Ren Bridge is one such example that offers to transfer BTC, Dogecoin, and ZCash between ETH, Luna, Solana, and Polygon.
Now, DApps require higher liquidity to attract more users. Cross-chain apps like AnySwap DEX offer the option of transferring multiple assets on different chains under one platform itself. Such a crypto cross-chain bridge makes using a DApp easier and more functional.
Now that blockchains are offering a chance to transfer tokens between chains, transferring NFTs between blockchains is becoming popular as well. Users get the option of minting NFTs on a chain with a lesser transaction fee. It also offers higher liquidity to the users.
According to the trust mechanism placed on the crypto cross-chain bridge, they can also be classified into this category. Trusted bridges make it mandatory for the users to allocate their assets to a custodian or a guardian that gets confirmation of transferring assets, locks in the native token, and mints the wrapped token. This whole type of cross-chain bridge relies on the compatibility and custodian trust factor. The custodians assigned to a user are chosen randomly, and the deposit proofs are created through smart contracts. Initially, there were problems that users raised about giving control to the custodians, but with the introduction of smart contracts, trust mechanism-based cross-chain bridges have become popular.
The benefits of cross-chain bridge:
Since you have gained knowledge about trusted mechanism bridges, you know that cross-chain bridges can seem to be centralized. This means that the need for a custodian or a guardian makes people doubt if these operators might gain power over the transfer of assets. Holding the frozen token, notifying the bridge about the transaction, verifying proofs of the transaction, minting and burning wrapped tokens, etc., are all the tasks that the custodians perform. All of such things may seem like centralization, which is moving away from the very principle of blockchain.
There may be cases where the power provided to the custodians can also be used to steal the users’ funds. Since the custodians get to freeze the user tokens, they may find a loophole to steal these funds and cause a major disruption in the bridge services. Although, cross-chain bridges try to tackle this issue by asking the custodians to sign some ‘bond.’
Decentralized bridges are not very popular in terms of providing higher liquidity to the users. The users of such bridges do not have much incentive to keep their assets locked on a blockchain and therefore add to the liquidity of a cross-chain bridge. This will cause the users to feel like the bridges are not providing them enough benefits.
While using a token on its native chain, the network provides censorship resistance to the users. But with the usage of cross-chain bridges, this censorship is usually lost, and the user funds might keep getting burnt or stay locked up even after the users demand options. This will cause a huge loss to the users, contributing to the disadvantages of using a crypto cross-chain bridge.
One of the biggest thefts occurred in the blockchain world when hackers stole around $320M from the Wormhole cross-bridge chain. This hack occurred only because of a small flaw in the smart contract used by the bridge to mint and burn the user funds.
Another case of technical vulnerabilities posed by using a crypto cross-chain bridge is Qubit Finance’s ETH-BSC bridge hack, where the hackers stole $80M by minting 206809 BNB coins. Decentralized bridges rely on smart contracts, which may have flaws. In such hacking cases, the bridges even had to beg the hackers to return the funds. Hackers usually exploit the immutable nature of the blockchain to carry out such activities. Smart contracts are only as secure as the developers make them, so a flaw in their initial coding can make people lose all of their investments in just one minute.
If you wish to transfer assets between the Polygon and ETH chains, then the Polygon PoS Bridge is the right choice. It can be considered the best cross-chain bridge in terms of offering a chance at the secure transfer of assets on the decentralized bridge. Users can transfer NFTs and assets from the Polygon sidechain to the ETH mainnet.
Binance bridge is one of the best platforms to access popular BSC DeFi apps like PancakeSwap, Venus, BeefyFinance, etc. It offers the option of transferring assets from the Binance smart chain to the Ethereum chain. It takes less processing time and costs less to make the transfer of assets. Users also have the liberty to redeem their original tokens anytime.
It primarily offers the option to transfer assets between Solana and Ethereum chains. Although, it also has the feature to transfer assets from multiple chains. It helps the users access the low-costing and higher throughput Solana chain. It also supports the transfer of NFTs and uses smart contracts to mint and burn assets.
It is a multiple-chain supporting cross-chain bridge. It offers a great opportunity to transfer BTC to the ETH chain. The best feature of this bridge is that it offers complete privacy in transactions.
Among the best cross-chain bridges, there is Synapse too. This bridge offers a chance to earn passive income through leveraging Synapse’s automated market maker. Users can also earn through staking and providing liquidity. It is a great platform to swap tokens and transfer assets.
It is a cross-chain bridge that supports EVM chains, ETH, and layer 2 networks. It offers a quick transfer of liquidity amongst the blockchains. Also, the users do not have to pay a very high fee.
Connext is a decentralized layer-2 scaling solution for blockchain networks that aims to enable fast and low-cost transactions by leveraging state channel technology. State channels are off-chain protocols that allow users to conduct transactions without submitting them to the blockchain, thus reducing transaction costs and increasing scalability. Connext provides a framework for building and managing state channels, facilitating the bi-directional transfer of assets and off-chain transactions between parties.
Want to know more about best cross chain bridges in detail. This article is for you Best Cross-Chain Bridges for 2023 👨💻
Now that you have learned about what is a cross-chain bridge, you must understand how important it is in taking blockchain technology forward. The option of interoperability it offers to the users makes it a highly required asset for the crypto world. Working upon some of its disadvantages, the crypto cross-chain bridge can become the next big thing in the crypto market. It offers the chance to use different assets on multiple blockchains and get the benefits of those blockchains, such as low gas fees. With the implementation of cross-chain bridges, the possibility of having an interconnected blockchain system is not too far-stretched. So, it can be concluded that the best crypto cross-chain bridges are the future of blockchain technology.
Cross-chain bridging works by establishing a connection between two or more blockchain networks, allowing assets or data to be transferred between them. Typically, a cross-chain bridge uses a combination of smart contracts, validators, or other mechanisms to lock assets on one blockchain while issuing corresponding assets or representations on another blockchain. This enables assets to be transferred from one blockchain to another and vice versa while maintaining security and integrity. The implementation and protocols may vary depending on the specific cross-chain bridge solution.
There are several examples of cross-chain bridges in the blockchain ecosystem. Some popular examples include RenVM, Polygon Bridge, Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), Thorchain, and Cosmos Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. These cross-chain bridges enable the transfer of assets or data between different blockchain networks, allowing for interoperability and collaboration across multiple chains.
Cross-chain bridges, like any other technology, are not immune to potential security risks. Some potential vulnerabilities or risks associated with cross-chain bridges include oracle attacks, smart contract vulnerabilities, malicious validators or consensus attacks, and other potential exploits. To mitigate these risks, cross-chain bridge developers implement various security measures such as multi-signature wallets, robust validation mechanisms, thorough auditing, and community-driven governance to ensure the security and integrity of cross-chain transactions.
A blockchain bridge is a technology or protocol that establishes a connection between two or more blockchain networks, enabling transfer of assets or data between them. It acts as an interoperability solution allowing seamless communication and transfer of assets or data across different blockchains. A blockchain bridge typically involves a set of smart contracts, validators, or other mechanisms to lock assets on one blockchain and issue corresponding assets or representations on another blockchain. This enables users to transfer assets or data between different blockchain networks, opening up new opportunities for cross-chain applications, services, and use cases.
Layer 1 Crypto Projects 2022 | Types of Cryptocurrency Scams | What is Miner Extractable Value | How to Make and Sell NFT | Types of Blockchain Nodes | Peer to Peer Money Transfer | Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology | Layer 1 Blockchain List | Blockchain Features and Benefits | How Does Blockchain Wallet Work | What is Proof of Work in Blockchain | Top Altcoins | What is Proof of Stake in Blockchain | What are the Benefits of Blockchain | Different Types of Nodes in Blockchain | What is Fiat Currency | What is Blockchain Nonce | Distributed Ledger Explained | Biggest NFT Marketplace | Ethereum Merge Importance | Best Metaverse Wallets | What Is Tokenomics | NFT Tracking Tools | Best Crypto Faucets | Ordinals NFTs